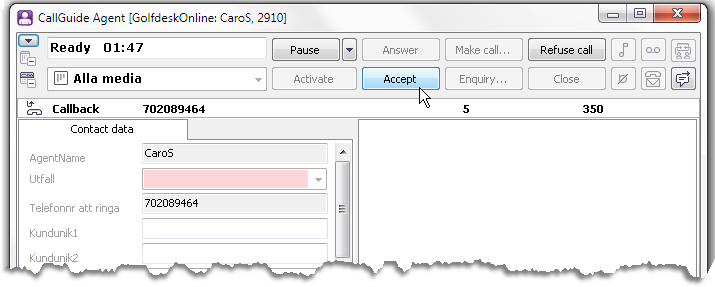
Callback is the type of outgoing telephony used to allow customers to be called at a later occasion – at their own request in IVR, from a web page or through a call with an agent. Information about the call to be made is saved by ACE as a callback record. This callback record contains i.a. the customer’s telephone number, and the time the customer wants to be called. At the time for making the call, the callback record is routed to a ready agent, in the same way as incoming calls in queue. Enquiries, like many other functions, function in the same way as for incoming calls. Unlike other media, an outgoing call cannot be parked or requeued.

The Accept button flashes when a callback record has been routed to you. When you click on the Accept button, ACE Agent will dial the telephone number that is specified in the callback record.
Other alternatives for accepting the dialling of an outgoing call are to
When the call is ocver you must give a mandatory fedbac, described in a separate section.
For contacts routed via waiting lists, you first select both list and contact:
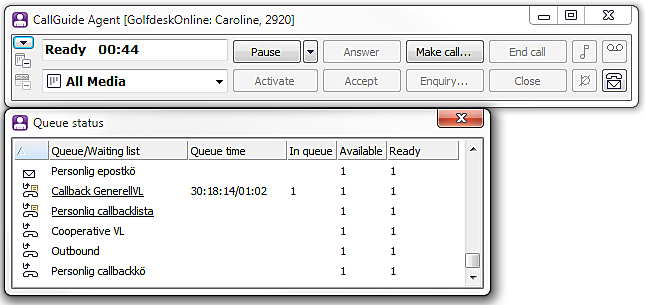
The Accept button flashes when you have selected a contact in a waiting list of callback records and the callback record has been routed to you.
Process the call in the same way as a callback call arriving via a queue.
If for some reason you cannot dial a callback record that has been routed to you, you can – if the Refuse call button is lit – choose to cancel dialling out. Access set in ACE Admin governs whether Refuse call is available.
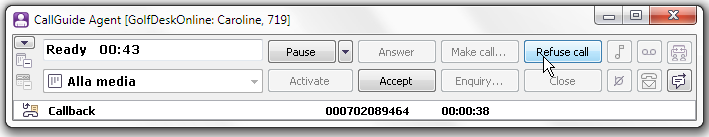
After a callback record has been refused, you will have to provide feedback for the contact based on a limited set of feedback values, described in a separate section.